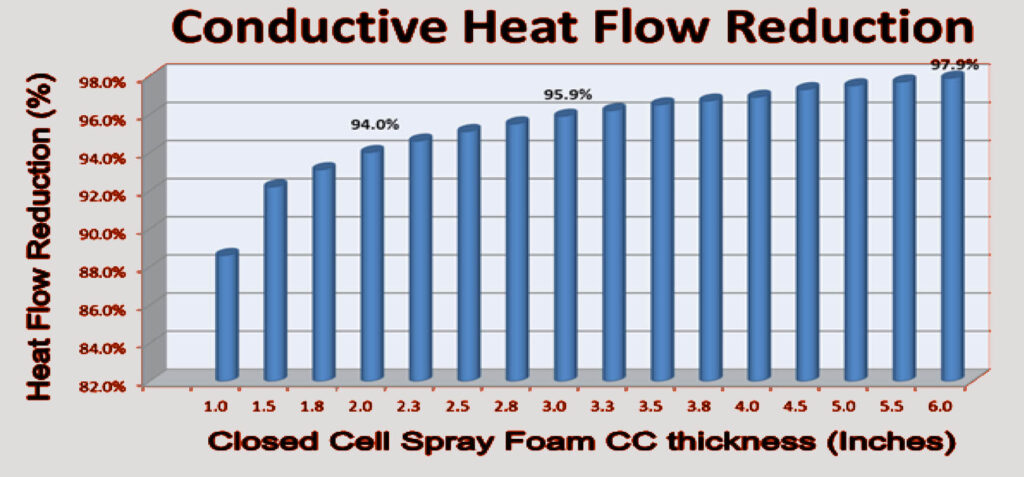
how thick does spray foam insulation need to be?
The thickness of spray foam insulation required depends on various factors, including the climate zone, the desired R-value (a measure of thermal resistance), the type of foam being used, and the application method.
For example, in a moderate climate zone, a closed-cell spray foam insulation with an R-value of 20 may require a thickness of 3.5 inches, while an open-cell spray foam insulation with an R-value of 20 may require a thickness of 5.5 inches.
It’s important to note that spray foam insulation should be installed by a professional who can assess the specific needs of your home or building and determine the appropriate thickness for your situation.
Discovering How R-Values are Tested to Ensure Energy Efficiency
R-values are an essential component of building insulation and energy performance. They indicate the measure of thermal resistance of a material and its ability to prevent heat transfer. The higher R-value a material has, the better it is at preventing heat loss. But have you ever wondered how the R-values of insulating materials are tested? In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at how R-values are tested and why Icynene insulation performs better despite having lower R-values compared to fiberglass insulation.
R-value testing is carried out in laboratories under ideal conditions. The conductive heat transfer property is measured, and convective heat transfer is not taken into account. In reality, however, wind flow and air infiltration play a big role when it comes to the energy performance of a building. This is where Icynene insulation excels over air-permeable insulation. Icynene provides superior energy performance due to its air barrier capability, even when compared to insulation with similar R-values.
The extensive computer modeling and field data have proven that the energy performance of Icynene insulation at lower R-values almost always outperforms fiberglass insulation in the field. This is because of its superior air-sealing ability and the reduction of convective heat transfer through air leakage. Hence, Spray Foam thermal performance in the field is superior in terms of the energy efficiency of a building. Therefore, lower R-values are usually recommended for Icynene insulation compared to fiberglass, and it still serves its purpose very well.
When it comes to R-value testing, two methods are commonly used. The first method is steady-state testing, where the heat flow through a material is measured in a laboratory setting. This method is useful for conducting standard testing but does not provide much data on real-world performance. The second method is known as the dynamic method and is considered the most accurate testing procedure. This method uses a range of heat fluxes and air temperatures, simulating real-world conditions more effectively.
Multiple factors affect R-value testing, such as the age of insulation, the type of material, and its density. A newer type of insulation, such as Icynene, may achieve superior performance despite its lower R-value due to its air-sealing properties and resistance to air leakage.
In conclusion, R-values are a crucial indicator of thermal resistance and help us determine the energy efficiency of a building. The R-value testing of insulating materials is carried out using either steady-state or dynamic methods. However, in reality, wind flow and air infiltration play a more significant role in energy performance. Icynene insulation has superior performance due to its air-sealing properties, making it an efficient alternative even with lower R-values than fiberglass. It is a step towards environmentally friendly and cost-effective insulation. As homeowners, contractors, or developers, it is essential to understand how R-values are tested to make well-informed decisions about insulation options to improve energy efficiency.